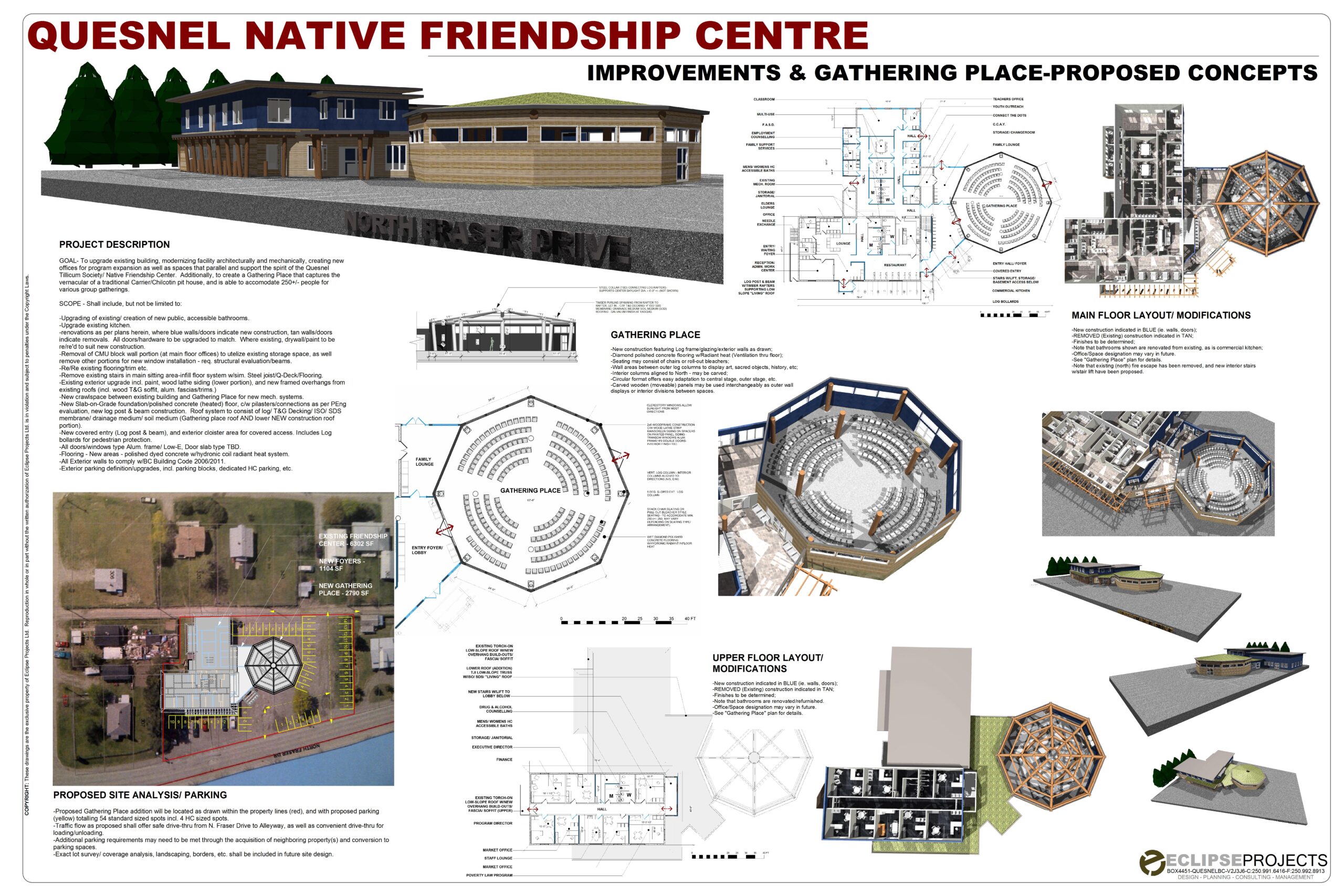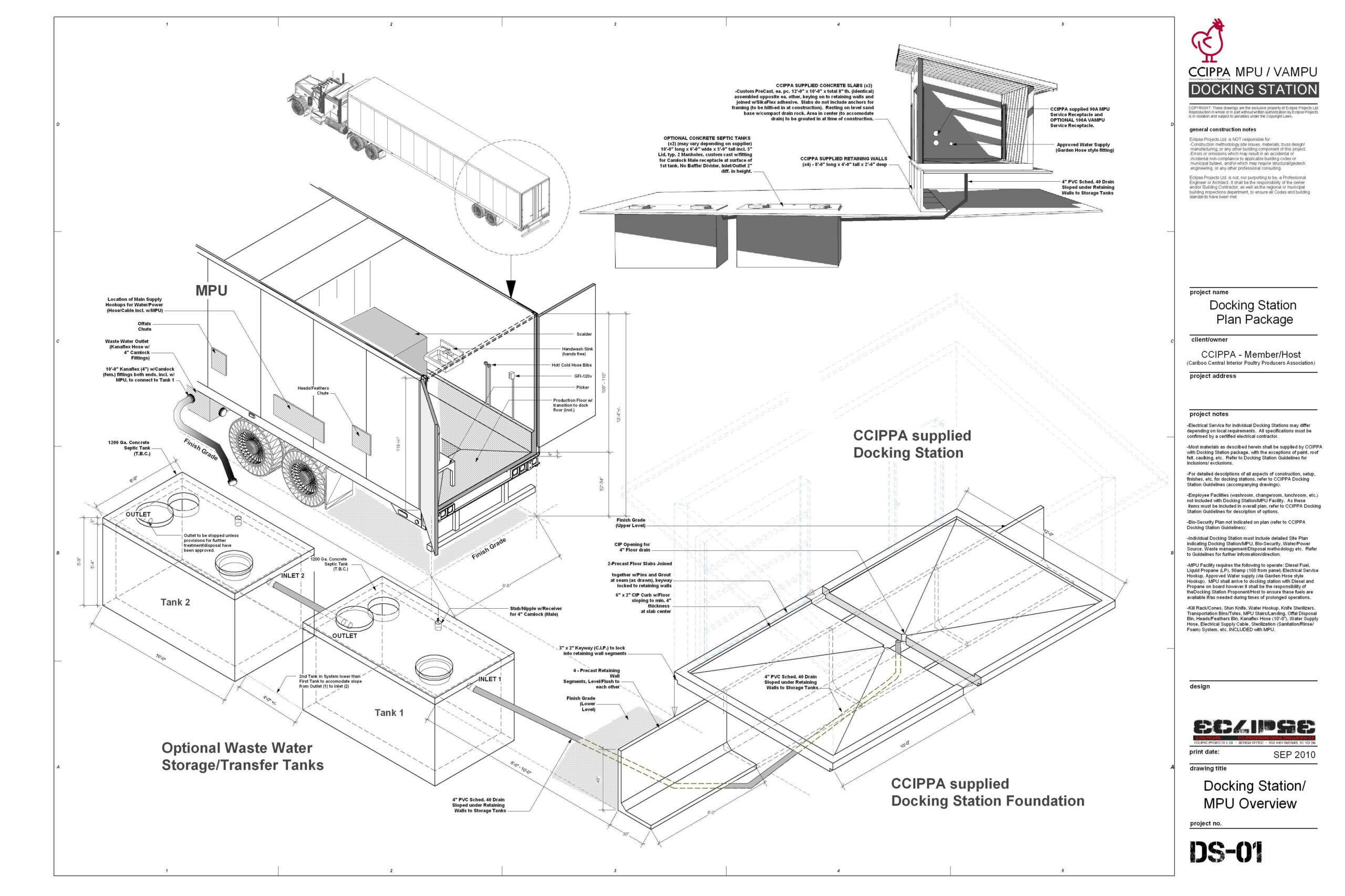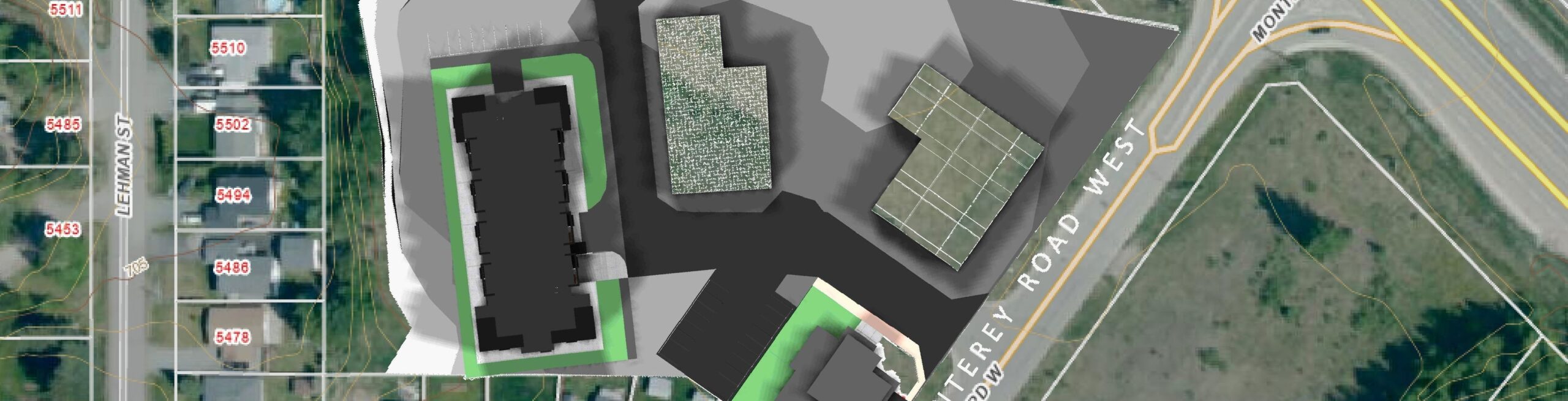
Space Planning
Space planning is a critical aspect of commercial design that ensures the efficient use of space to meet the functional needs of businesses. Space planning involves organizing and arranging interior spaces to optimize functionality, efficiency, and aesthetics. It is a strategic process that takes into account the spatial requirements, flow of movement, and the specific activities that will occur within the space.
Key Principles of Space Planning
- Functionality: The primary goal of space planning is to ensure that the space meets the practical needs of its users. This includes considering the purpose of each area and ensuring that it is designed to support the activities that will take place there.
- Flow and Circulation: Efficient circulation is crucial in commercial spaces. Design pathways and layouts that allow for smooth movement of people and goods, minimizing bottlenecks and ensuring easy access to different areas.
- Flexibility: Commercial spaces should be adaptable to changing needs. Flexible design allows for easy reconfiguration and adjustment of spaces to accommodate different functions and activities.
- Aesthetics: While functionality is key, aesthetics also play a significant role in space planning. Create visually appealing environments that reflect the brand identity and enhance the overall experience for users.
- Compliance and Safety: Ensure that the design complies with relevant building codes and safety regulations. This includes accessibility standards, fire safety measures, and structural integrity.
Steps in the Space Planning Process
- Needs Assessment: Begin by understanding the specific needs of the business. This includes identifying the activities that will take place, the number of people using the space, and any special requirements.
- Space Inventory: Conduct an inventory of the available space. Measure dimensions, identify structural elements, and take note of any existing features that will impact the design.
- Zoning: Divide the space into different zones based on function. For example, in an office, you might have zones for workstations, meeting rooms, break areas, and storage.
- Layout Design: Develop layout options that arrange the zones efficiently. Consider factors such as proximity, accessibility, and flow of movement. Use floor plans and sketches to visualize different arrangements.
- Furniture and Equipment: Plan for the placement of furniture and equipment. Ensure that there is adequate space for movement and that the furniture supports the intended activities.
- Review and Adjust: Review the proposed layout with stakeholders and make adjustments based on feedback. Ensure that the final design meets all functional, aesthetic, and regulatory requirements.
Effective space planning is essential for creating functional, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing commercial spaces. For the Eclipse Project, applying these principles can lead to the development of well-organized and adaptable environments that meet the specific needs of businesses.
Innovation Unleashed: Empowering Your Ideas to Eclipse Boundaries.